

Data for solar data and conditions from NOAA SWPC, solar flux fromĪnd world map/globes/solar system from Fourmilab (credit given).Data for Solar Flare Probability is from University of Bradford (used with permission).
Data for VHF Conditions is from DXrobot - Gouda, Make More Miles on VHF, and Andy (G7IZU) (all used with permission).The only sure-fire way to determine if the bands are open is to fire up that HF rig and get on the air! Of course, actual conditions at your location depend on a lot ofĪdditional items. HF Propagation predictions are just that, predictions calculated using the available data.World sunlight maps and globes, moon view globe, graphs and plots, and selectable current solar system planet locations. HF Conditions, VHF Conditions, EME degradation, selectable and fixed MUF, selectable K index (impacts conditions), signal noise and geomagnetic conditions, current secletable solar images, Solar banners are available in 19 different configurations (see below), with variations of solar indicies and measurements,.
#Solar flux download#
You can download from this linkĭisplaying Solar-Terrestrial Data Panels on your site, computer, or other personal deviceĪdd Solar-Terrestrial Data to your Website
#Solar flux pdf#
#Solar flux how to#
pdf presentation that contains tutorials and information on understanding radio propagation, and how to use all the data contained in the solar panels.For current Space Weather and HF Propagation Conditions, and MUF Maps click here.For Understanding/Using Solar-Terrestrial Data, Solar Images, and HF Tutorials click here.For NOAA's SWPC WSA-Enlil Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) Solar Wind Prediction Model click here.For Online MOF/LOF HF Propagation Prediction Tool, and conversion tools click here.Use the buttons at the top and bottom of the page to navigate, or use the following links:.HF Propagation Tools and Solar Data are now on multiple pages for faster loading

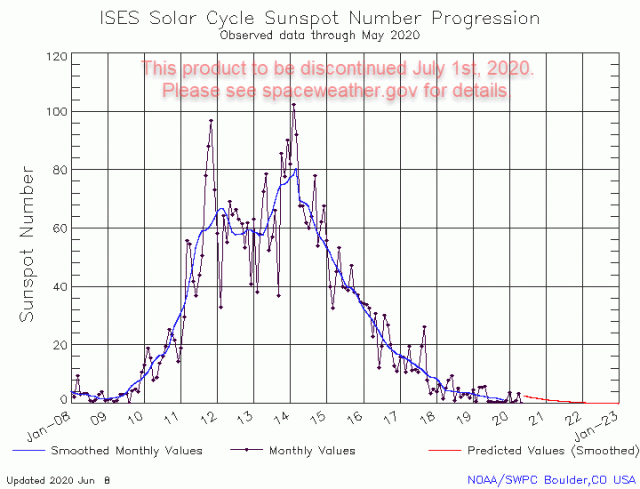
See FAQ page for configeration information. NWRA Effective Smoothed Sunspot Numbers (SNe) is still available Its the same data and value just much earlier (like 12 hours) than the old NOAA SWPC source. Smoothed Sunspot data (SN) from NOAA SWPC is now updated at 00:00 UTC every day on all banners and xml/rss data.
#Solar flux series#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
